Biology : Zoology XI
UNIT FOUR : KINGDOM PROTISTA
Class : 11
Kingdom :- Animalia
Phylum :- Protozoa
class :- Ciliata
Genus :- Paramecium
Species :- caudatum
(HSEB science notes for students of grade 11 )
Sexual and Asexual reproduction in Paramecium caudatum
Paramecium is an unicellular, miscroscopic Eukaryotic protozoan. It's Reproduction of two type i.e sexual and asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction in paramecium occurs by Transverse binary fission under favourable condition and sexual reproduction occurs by conjugation under unfavourable condition after about 300 times of binary fission when the paramecium becomes weak.
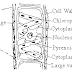
Paramecium Caudatum reproduce asexually by the process of Transverse Binary fission during favourable condition. In this process a fully grown Paramecium divides into two daughter paramecia.
Before the fission, the paramecium stops feeding and it's oral groove disappears. It's macronucleus elongates and divides amitotically whereas it's micro-nucleus divides mitotically. Transverse constriction occurs and cytoplasm divides into two equal halves. The original contractile vacuole of paramecium get distributed into each half to form new posterior contractile vacuole at anterior half and another new anterior contractile vacuole at posterior half. After that, new oral groove appears in each half. Finally, two equal sized daughter paramecia are formed with all parts. The anterior daughter paramecia is called protor and new posterior formed daughter paramecia is called opisthe.
This way binary fission occurs in paramecia which last/completes in about 20-25 minutes according the condition. In 24 hours a paramecia divides 3-5 times.
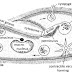
It temporary union of two morphological similar but physiologically different paramecia. Conjugation in paramecium takes place in unfavorable condition after about 300 times of binary fission when the paramecium becomes weak.
Before this conjugation process, two paramecia of opposite mating type of same species come attach together with their ventral surface. Both of them are adhered together by a sticky substance secreted by cilia. At last they are called as conjugants.
The nuclear changes that occurs in each conjugant during conjugation in Paramecium caudatum are as follows :
1. At first, the macro-nucleus starts to disappear and micro-nucleus remains same in each conjugants.
2. After that the micro-nucleus undergo reduction division (meiosis) to form 4 micro-nuclei.
3. Among 4 micro-nuclei 3 starts to degenerate leaving one which enlarges.
4. The remaining one marcronucleus under go unequall division forming large stationary female pro-nucleus and small migratory male pro-nucleus in each of the conjugants.
5. The male pro-nucleus migrate toward the opposite female pro-nucleus through cytoplasmic bridge and get exchanged between the two conjugants.
6. Due to fusion between male and female pro-nucleus synkaryon is formed.
7. The conjugants get separated from each other. Now they are called as ex- conjugants.
8. Each ex-conjugants divide 3 times by mitotic division to form 8 micronuclei.
9. Among the 8 micro-nuclei 4 enlarges and they are called macronuclei and remaining 4 are called micronuclei.
10. Among 4 micronuclei 3 starts to degenerate leaving one.
11. The remaining oone macronucleus divide by mitotic and undergo binary fission to form 2 paramecia having 2 macronuclei and 1 micronucleus.
12. Again it divide by binary fission and again forms 2 paramecia having 1 macro-nuclei and 1 micro-nuclei.
Significance of conjugation in short :
So, this way from each conjugant 4 paramecia are form. It helps to start vitality in them and don't let them extinct and also provide them with adaptability strength in changing environment.
UNIT FOUR : KINGDOM PROTISTA
Class : 11
 |
| Paramecium caudatum |
Kingdom :- Animalia
Phylum :- Protozoa
class :- Ciliata
Genus :- Paramecium
Species :- caudatum
(HSEB science notes for students of grade 11 )
Sexual and Asexual reproduction in Paramecium caudatum
Paramecium is an unicellular, miscroscopic Eukaryotic protozoan. It's Reproduction of two type i.e sexual and asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction in paramecium occurs by Transverse binary fission under favourable condition and sexual reproduction occurs by conjugation under unfavourable condition after about 300 times of binary fission when the paramecium becomes weak.
Transverse Binary fission in Paramecium Caudatum
Paramecium Caudatum reproduce asexually by the process of Transverse Binary fission during favourable condition. In this process a fully grown Paramecium divides into two daughter paramecia.
Before the fission, the paramecium stops feeding and it's oral groove disappears. It's macronucleus elongates and divides amitotically whereas it's micro-nucleus divides mitotically. Transverse constriction occurs and cytoplasm divides into two equal halves. The original contractile vacuole of paramecium get distributed into each half to form new posterior contractile vacuole at anterior half and another new anterior contractile vacuole at posterior half. After that, new oral groove appears in each half. Finally, two equal sized daughter paramecia are formed with all parts. The anterior daughter paramecia is called protor and new posterior formed daughter paramecia is called opisthe.
This way binary fission occurs in paramecia which last/completes in about 20-25 minutes according the condition. In 24 hours a paramecia divides 3-5 times.
Sexual reproduction (Conjugation in Paramecium caudatum)
The process of conjugation (explain) in paramecium caudatum is described below :
It temporary union of two morphological similar but physiologically different paramecia. Conjugation in paramecium takes place in unfavorable condition after about 300 times of binary fission when the paramecium becomes weak.
Before this conjugation process, two paramecia of opposite mating type of same species come attach together with their ventral surface. Both of them are adhered together by a sticky substance secreted by cilia. At last they are called as conjugants.
The nuclear changes that occurs in each conjugant during conjugation in Paramecium caudatum are as follows :
1. At first, the macro-nucleus starts to disappear and micro-nucleus remains same in each conjugants.
2. After that the micro-nucleus undergo reduction division (meiosis) to form 4 micro-nuclei.
3. Among 4 micro-nuclei 3 starts to degenerate leaving one which enlarges.
4. The remaining one marcronucleus under go unequall division forming large stationary female pro-nucleus and small migratory male pro-nucleus in each of the conjugants.
5. The male pro-nucleus migrate toward the opposite female pro-nucleus through cytoplasmic bridge and get exchanged between the two conjugants.
6. Due to fusion between male and female pro-nucleus synkaryon is formed.
7. The conjugants get separated from each other. Now they are called as ex- conjugants.
8. Each ex-conjugants divide 3 times by mitotic division to form 8 micronuclei.
9. Among the 8 micro-nuclei 4 enlarges and they are called macronuclei and remaining 4 are called micronuclei.
10. Among 4 micronuclei 3 starts to degenerate leaving one.
11. The remaining oone macronucleus divide by mitotic and undergo binary fission to form 2 paramecia having 2 macronuclei and 1 micronucleus.
12. Again it divide by binary fission and again forms 2 paramecia having 1 macro-nuclei and 1 micro-nuclei.
Significance of conjugation in short :
So, this way from each conjugant 4 paramecia are form. It helps to start vitality in them and don't let them extinct and also provide them with adaptability strength in changing environment.
(HSEB science notes for students of grade 11 )






0 comments: