(science Notes for HSEB Grade 11and 12 students for botany chemistry physics and zoology)
Theory : This method can be used to determine the equivalent weight of a metal which can evolve hydrogen gas with dil mineral acid like HCl , H2SO4. Some metals like Zn, Mg etc which lie above hydrogen in the electrochemical series can evolve hydrogen gas.
In this process, first definite weight of metal is taken and treated with excess of dil mineral acid. Due to this hydrogen gas is produced. The volume of gas obtained is at the lab condition of temperature and pressure so it is converted to volume at NTP by combined gas equation i.e P1 V1/T1= P2 V2/T2.
After it is converted to volume at NTP it is then converted to mass using mole concept or following formula :
Mass of hydrogen = Volume of hydrogen at NTP (in ml) . 0.000089
From the mass of hydrogen the equvalent weight of metal can be obtained by following formula :
Equivalent weight of metal = (mass of metal / mass of hydrogen ) . 1.008
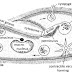
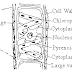
Procedure : A peice of metal is taken and it's weight is measured by using chemical balance. Then it is converted to "V" shaped so that it sinks in water and it is tied with a thread and kept in a large beaker filled with water. A small short funnel is inverted over the metal inside the beaker in such a way that the steam of the funnel is completly inside the water. An eudiometric tube is taken and it is filled half with acid and remaining half with water. Then it is inverted over the funnel such that there is no bubble left in the tube and it is clamped with a stam. The acid inside the tube comes down slowly and reacts with the metal and hydrogen gas is evolved which is collectef in the eudiometric tube above the water. The apparatus is left for the completion if the reaction. In the meanwhile the temperature and pressure of the lab is noted. After the completion if the reaction i.e when hydrogen gas stops producing, the tube is shaken for a while to collect all the bubble of hydrogen gas into the tube. Then the tube is taken out of the beaker, closing the mouth of the tube carefully and the volume of hydrogen is is noted by kepping the tube inside the water in a tall jar. The level of water inside and outside the tube is made equal so that the pressure inside and outside becomes same. Then is volume of hydrogen at lab condition of temperature and pressure is converted to volume at NTP and to mass. From the mass of the hydrogen , the equivalent weight of the metal can be determined.
Theory : This method can be used to determine the equivalent weight of a metal which can evolve hydrogen gas with dil mineral acid like HCl , H2SO4. Some metals like Zn, Mg etc which lie above hydrogen in the electrochemical series can evolve hydrogen gas.
In this process, first definite weight of metal is taken and treated with excess of dil mineral acid. Due to this hydrogen gas is produced. The volume of gas obtained is at the lab condition of temperature and pressure so it is converted to volume at NTP by combined gas equation i.e P1 V1/T1= P2 V2/T2.
After it is converted to volume at NTP it is then converted to mass using mole concept or following formula :
Mass of hydrogen = Volume of hydrogen at NTP (in ml) . 0.000089
From the mass of hydrogen the equvalent weight of metal can be obtained by following formula :
Equivalent weight of metal = (mass of metal / mass of hydrogen ) . 1.008
Procedure : A peice of metal is taken and it's weight is measured by using chemical balance. Then it is converted to "V" shaped so that it sinks in water and it is tied with a thread and kept in a large beaker filled with water. A small short funnel is inverted over the metal inside the beaker in such a way that the steam of the funnel is completly inside the water. An eudiometric tube is taken and it is filled half with acid and remaining half with water. Then it is inverted over the funnel such that there is no bubble left in the tube and it is clamped with a stam. The acid inside the tube comes down slowly and reacts with the metal and hydrogen gas is evolved which is collectef in the eudiometric tube above the water. The apparatus is left for the completion if the reaction. In the meanwhile the temperature and pressure of the lab is noted. After the completion if the reaction i.e when hydrogen gas stops producing, the tube is shaken for a while to collect all the bubble of hydrogen gas into the tube. Then the tube is taken out of the beaker, closing the mouth of the tube carefully and the volume of hydrogen is is noted by kepping the tube inside the water in a tall jar. The level of water inside and outside the tube is made equal so that the pressure inside and outside becomes same. Then is volume of hydrogen at lab condition of temperature and pressure is converted to volume at NTP and to mass. From the mass of the hydrogen , the equivalent weight of the metal can be determined.





0 comments: